Overview
In November 2021, President Biden signed H.R. 3684, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) into law. Often referred to as the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), IIJA authorizes $1.2 trillion over five federal fiscal years (FY 2022-2026) for surface transportation projects and programs, as well as water, wastewater, energy transmission, resilience, and broadband. IIJA reauthorizes the Fixing America’s Surface Transportation Act (FAST Act) while expanding existing grant programs and adding new grants.
U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT) priorities—reducing inequities across transportation systems, making the transportation system safer, and designing for the future—are reflected in the new transportation grants. IIJA offers $550 billion in new investments above baseline spending levels. USDOT is one of several federal agencies providing funding through the act along with the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Energy, Homeland Security, Health and Human Services, Interior, and the Environmental Protection Agency.
IIJA Transportation Funding
Transportation funding constitutes $661.1 billion of total IIJA funds. $284 billion is new funding, with the remaining $377.1 billion as baseline funding at a 23.6 percent increase over FY2022 levels. Three sources of funding are used:
- Highway Trust Fund dollars from the Highway Account or Transit Account of the Highway Trust Fund (estimated $383.4 billion)
- Guaranteed Appropriations added by bipartisan agreement and used to increase funding for existing programs or to fund new programs (estimated $184.3 billion)
- General Fund dollars that are authorized for use yet require future action by the Appropriations Committee to be made available (estimated $93.5 billion)
The following table provides an estimated breakdown of anticipated federal funds for the region. Estimates are likely to change as programs are finalized and updated census data is used for apportionments. In addition to the figures in the table, the IIJA extends the Passenger Rail Investment and Improvement Act of 2008 (PRIIA) through 2030. This extension provides $150 million annually towards WMATA’s Capital Program which is equally matched by the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia.
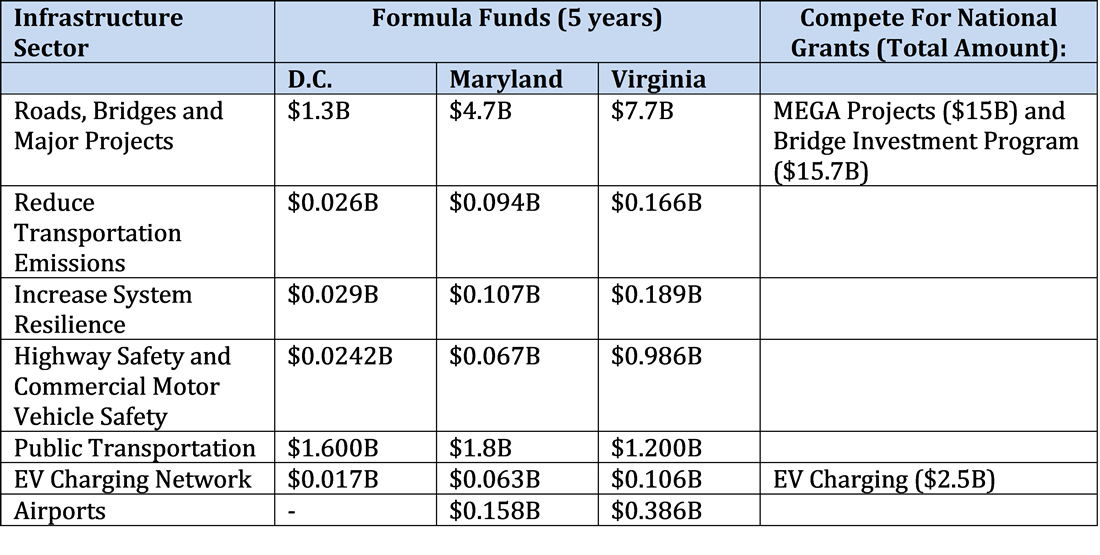 Source: TPB
Source: TPB
IIJA Expanded and New Federal Grant Programs
The following grant programs will issue notices of funding opportunity (NOFO) announcements containing eligibility, application, program requirements, and deadlines. The USDOT IIJA page lists a schedule of grant notifications that are regularly updated.
Expanded/Existing Grants:
- Rebuilding American Infrastructure with Sustainability and Equity (RAISE) Grants ($15 billion, expanded) – RAISE grants support surface transportation projects of local and/or regional significance.
- Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Low and No Emission Bus Programs ($5.6 billion, expanded) – This competitive program provides funding to state and local governmental authorities for the purchase or lease of zero-emission and low-emission transit buses as well as acquisition, construction, and leasing of required supporting facilities.
- FTA Buses and Bus Facilities Competitive Program ($2.0 billion, expanded) – This program provides competitive funding to states and direct recipients to replace, rehabilitate, and purchase buses and related equipment and to construct bus-related facilities including technological changes or innovations to modify low or no emission vehicles or facilities.
- Capital Investment Grants (CIG) Program ($23 billion, expanded) – Funds are for investments in new high- capacity transit projects communities choose to build.
- Infrastructure for Rebuilding America (INFRA) Grants ($14 billion, expanded) – INFRA grants will offer needed aid to freight infrastructure by providing funding to state and local governments for projects of regional or national significance.
- Port Infrastructure Development Program ($2.25 billion, expanded) – This program increases investment in coastal ports and inland waterways, helping to improve the supply chain and enhancing the resilience of our shipping industry.
- Ferry Program ($150 million, existing) – This program retains the $30 million per year passenger ferry program for ferries that serve urbanized areas.
New Grants
- Safe Streets for All ($6 billion, new) – This program will provide funding directly to local and tribal governments to support their efforts to advance “Vision Zero” plans and other improvements to reduce crashes and fatalities, especially for cyclists and pedestrians.
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Terminal Program ($5 billion, new) – The terminal discretionary grant program will provide funding for airport terminal development and other landside projects.
- MEGA Projects ($15 billion, new) – The new National Infrastructure Project Assistance grant program will support multi-modal, multi-jurisdictional projects of national or regional significance.
- Promoting Resilient Operations for Transformative, Efficient, and Cost-saving Transportation (PROTECT) Program ($8.7 billion, new) – PROTECT will provide $7.3 billion in formula funding to states and $1.4 billion in competitive grants to eligible entities to increase the resilience of our transportation system, including evacuation routes, coastal resilience, making existing infrastructure more resilient, or efforts to move infrastructure to nearby locations not continuously impacted by extreme weather and natural disasters.
- Electric or Low Emitting Ferry Program ($500 million, new) – This competitive grant program will support the transition of passenger ferries to low or zero emission technologies.
- Rural Ferry Program ($2 billion, new) – A competitive grant program that will ensure that basic essential ferry service continues to be provided to rural areas by providing funds to States to support this service.
- Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) competitive grants for nationally significant bridges and other bridges ($15.77 billion, new) – This new competitive grant program will assist state, local, federal, and tribal entities in rehabilitating or replacing bridges, including culverts. Large projects and bundling of smaller bridge projects will be eligible for funding.
Resources
This summary draws from resources available from USDOT, FHWA, and FTA websites, White House fact sheets, and publications produced by the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), National Association of Regional Councils (NARC), National Association of Counties (NACo), Association of Metropolitan Planning Organizations (AMPO), the ENO Foundation, and others.
Visit the TPB Technical Committee July meeting page for a copy of the full IIJA memorandum.
For more information and the latest updates on grant programs and funding levels, visit the following websites:
White House BIL Highway Provisions Factsheets
White House BIL Guidebook
USDOT BIL Homepage
FHWA BIL Homepage
FTA BIL Homepage